- Published on
Fundamentals of C/C++ Multithreading Programming
- Authors

- Name
- light-city
Fundamentals of C/C++ Multithreading Programming
1. Basic Issues
- Will a thread crashing lead to process termination? Or does a crash of a thread within a process affect other threads?
Answer: Generally, each thread is an independent execution unit with its own context and stack. A crash in one thread does not affect other threads. However, typically, a thread crash might generate an error within the process, such as a Segment Fault error in the Linux operating system. This error generates a signal, and the default action of the operating system for this signal is to terminate the process, resulting in the destruction of the entire process along with any other threads within it.
- How to investigate high CPU usage in a Linux process?
In actual development, improper program logic can sometimes cause a thread to spin (such as in an infinite loop), leading to high CPU usage for that process. This not only causes system lag but also wastes CPU resources. How can we locate and troubleshoot the thread causing high CPU usage?
In Linux, we can use a combination of the pstack and top commands to troubleshoot such issues.
2. Basic Commands
- pstack
In Linux systems, the pstack command can be used to view the number of threads in a process and the call stack for each thread.
pstack pid
Set pid to the ID of the process you want to examine.
- top
It displays processes using the most CPU, finds the process ID with the highest CPU usage, and then uses:
top -p pid
Observe the CPU, memory, and load of the specified PID.
Here is some information:
top - 19:30:05 up 6:15, 1 user, load average: 0.85, 0.71, 0.61
Tasks: 1 total, 0 running, 1 sleeping, 0 stopped, 0 zombie
%Cpu(s): 8.1 us, 2.9 sy, 0.0 ni, 87.8 id, 0.0 wa, 0.0 hi, 1.1 si, 0.0 st
KiB Mem : 20412976 total, 10960136 free, 5416592 used, 4036248 buff/cache
KiB Swap: 2097148 total, 2097148 free, 0 used. 14315608 avail Mem
The first line shows task queue information
| Task Queue Information | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 9:30:05 | Current time |
| 6:15 min | User online time |
| 1 user | Number of users |
| load average: 0.85, 0.71, 0.61 | System load, average length of the task queue. Average load 1 minute ago, 5 minutes ago, and 15 minutes ago |
The second line is process information
| Process Information | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Tasks: 1 total | Total number of processes |
| 0 running | Number of processes running |
| 1 sleeping | Number of processes sleeping |
| 0 stopped | Number of processes stopped |
| 0 zombie | Number of zombie processes |
The third line is CPU information
| CPU Information | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 8.1 us | Percentage of CPU time spent in user space |
| 2.9% sy | Percentage of CPU time spent in kernel space |
| 0.0% ni | Percentage of CPU time spent on processes whose priority has been modified in user space |
| 87.8% id | Percentage of idle CPU time |
| 0.0% wa | Percentage of CPU time spent waiting for I/O |
| 0.0% hi | Hardware interrupts |
| 1.1% si | Software interrupts |
| 0.0%st | Real time |
The fourth and fifth lines are memory information.
| Physical Memory Information | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Mem: 20412976 total | Total physical memory |
| 5416592 used | Total used physical memory |
| 10960136 free | Total free physical memory |
| 4036248 buffers/cache | Memory used for kernel buffers/cache |
| Swap Information | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Swap: 2097148 total | Total swap memory |
| 0k used | Used swap memory |
| 2097148 free | Free swap memory |
| 14315608 cached | Cached swap memory |
How can we use the top command to locate CPU usage for each thread in a problem process?
Use -H. The -H option of the top command displays the thread mode of each process.
For example:
top -p 2085 -H
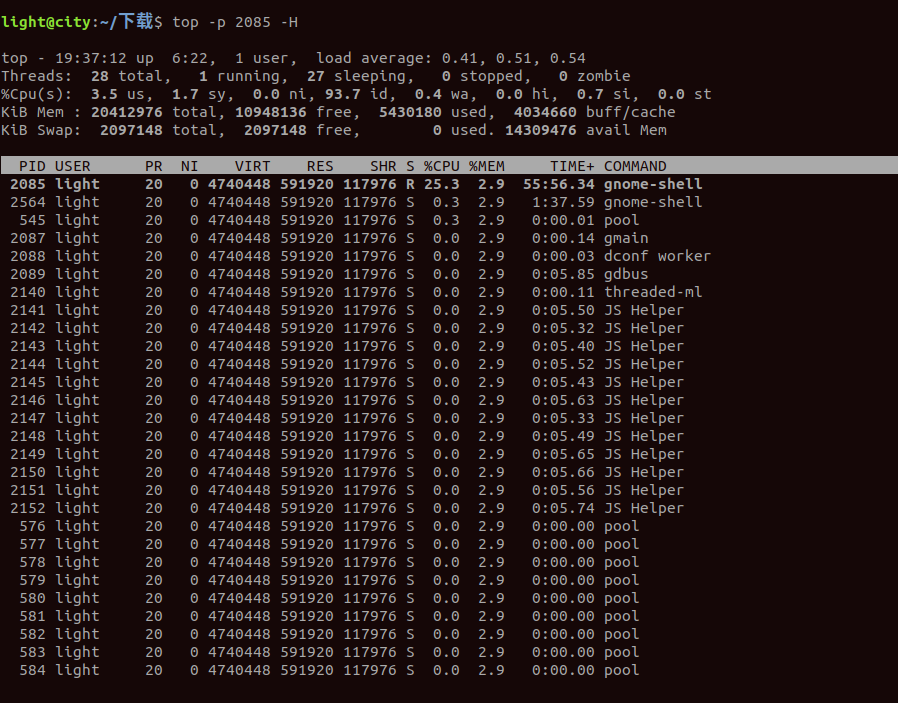
From the above image, it's evident that the thread with PID 2085 has the highest CPU usage. Next, pinpoint whether there are any abnormalities in the code of this thread causing excessive CPU usage.
Combining the above pstack information, for instance:
pstack 2085
In the output of pstack for each thread, by cross-referencing our program's source code, we can identify whether there are logic blocks in that thread spending most of its time spinning. Then, modifying and optimizing these logics can resolve the issue of high CPU usage. In general, non-working threads should preferably be suspended using lock objects rather than spinning, as this can improve system resource utilization.